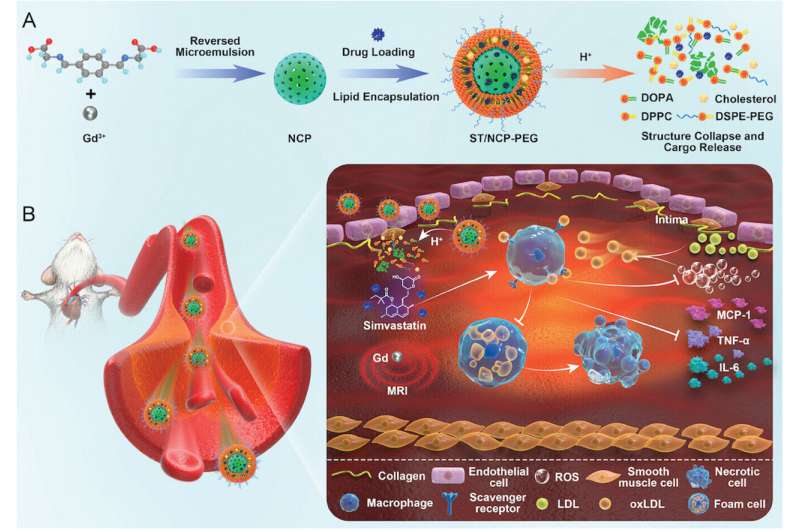
Schematic diagram of A) formation process of ST/NCP-PEG and degradation of pH structure under acidic microenvironment. B) a pH-responsive and MRI-functional ST/NCP-PEG nanomedicine that enables the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Credit: Small (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202401659
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque in the arteries that causes them to narrow. It is the leading cause of ischemic heart disease (IHD) and ischemic stroke (IS), both of which contribute to 17.9 million deaths from cardiovascular disease each year worldwide. width. The incidence of atherosclerosis has been increasing steadily over the past three decades, especially in the younger population. This increase is driven by lifestyle factors such as junk food, lack of exercise, smoking and alcohol consumption.
In Singapore, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death, accounting for 31% of deaths by 2022, and an estimated three-fold increase in obesity-related heart attacks by 2050.
Common methods used for imaging atherosclerotic plaques include methods such as intravascular ultrasound, coronary angiography, computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, these methods have limitations in resolution, invasiveness, and most importantly, the ability to provide targeted treatments.
- Intravascular ultrasound, uses an ultrasound probe through a catheter inside a blood vessel to visualize the walls of blood vessels for a detailed examination of the size and shape of the plaque. However, this method is invasive and only works on large blood vessels with limited spatial resolution.
- Coronary angiography, uses X-ray images and dye injection that provides contrast to visualize blood vessels and detect blockages caused by plaque.
- Similar to X-ray coronary angiography, computed tomography angiography uses ionizing radiation and dye injection to obtain more detailed images of the blood vessels.
- MRI provides the highest quality images of blood vessels and plaque morphology among the four imaging modalities.
There are currently no drugs or treatments that can specifically target atherosclerotic plaques, significantly reduce plaque burden or reverse atherosclerosis. Patients at high risk of CVD are often prescribed medications that can stabilize plaques, including statins that lower blood cholesterol, anti-platelet agents such as aspirin to reduce the risk of plaque formation in the area of plaques, when ace inhibitors and beta-blockers are used. to control high blood pressure.
A team at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (NUS Medicine) has developed a nanoparticle technology that provides an effective solution for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis, in a non-invasive manner. This new theranostic method, published in the journal Smallrepresents a major advance in the field of cardiovascular medicine as it offers more promising alternatives to current medical methods for the management of atherosclerosis.
Led by Associate Professor Wang Jiong-Wei from the Department of Surgery, the Nanomedicine Translational Research Program at NUS Medicine, and the Cardiovascular Research Institute (CVRI), this multidisciplinary study was carried out in collaboration with Professor James Kah of Department of Biomedical Engineering and Professor. Liu Bin from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering under the College of Design and Engineering NUS, and Professor Liu Xiaogang from the Department of Chemistry in the NUS Faculty of Science.
The team has developed a nanoparticle that addresses these challenges; The newly developed nanoparticle is able to diagnose atherosclerosis, target atherosclerotic plaques, and deliver therapeutic agents directly to prevent the progression of atherosclerosis in early treatment models.
Made up of nanoscale coordination polymers (NCP) and a pH-responsive linker, the nanoparticles work by specifically breaking down the acidic environment of atherosclerotic plaques, releasing gadolinium—a contrast agent for of MRI-for real-time imaging of the depth of the plaque while simultaneously providing. Simvastatin, a water-soluble drug with anti-inflammatory properties and anti-ROS (reactive oxygen species) that contributes to the stabilization and treatment of plaque, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Compared to the administration of the same dose of Simvastatin, nanoparticles can deliver the drug 1000 times to the plaques, thus improving the therapeutic effect while reducing the systemic effects.
“Overall, our nanoparticles offer a promising method for the non-invasive diagnosis, monitoring and targeted treatment of atherosclerosis, a major advance that could pave the way for a new era of cardiovascular care. ,” said Asst Prof Wang, Principal Investigator, Translational Nanomedicine. Research Programme, NUS Medicine.
This proof-of-concept study shows great potential for the new method and the team wants to validate their research before moving on to clinical trials.
Additional information:
Yuanzhe Lin et al, Dual-Function Nanoscale Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles for Targeted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Delivery in Atherosclerosis, Small (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202401659
Newspaper articles:
Small
Provided by the National University of Singapore
Excerpt: Nanoparticle technology shows promise for diagnosis and targeted therapy of atherosclerosis (2024, September 18) retrieved on September 18, 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-09 -nanoparticle-technology-diagnosis-treatment-atherosclerosis.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any legitimate activity for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. Content is provided for informational purposes only.
#Nanoparticle #technology #shows #promise #targeted #diagnosis #treatment #atherosclerosis