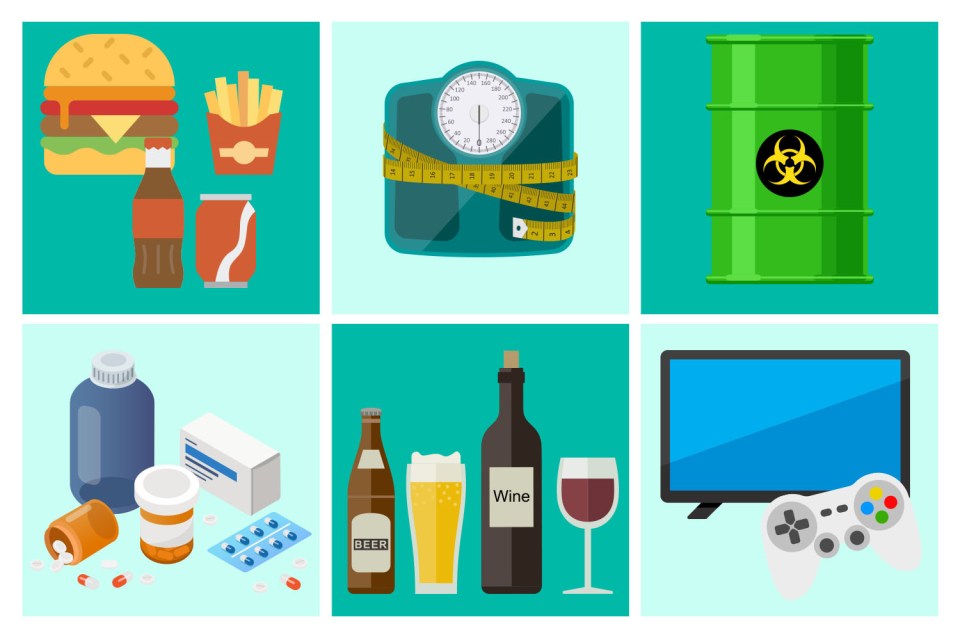
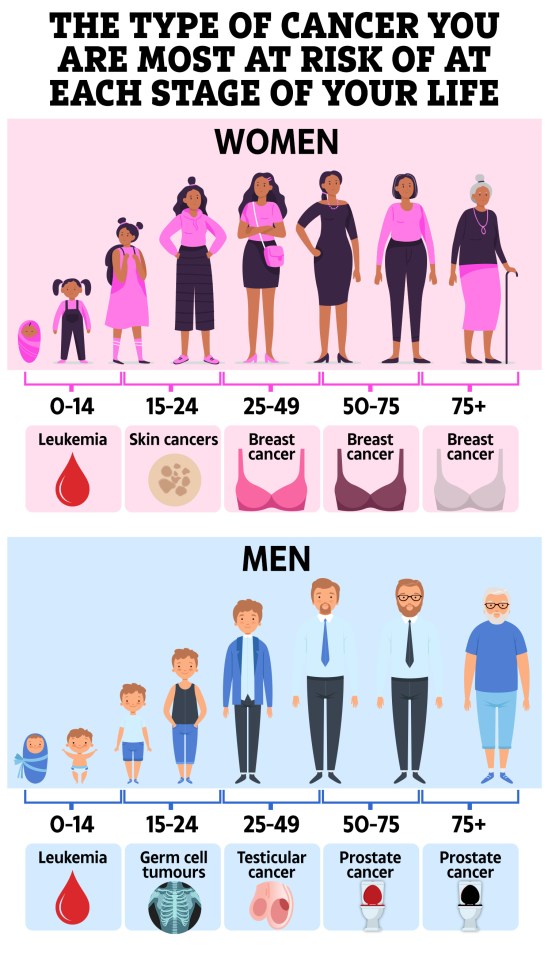
Six lifestyle factors are behind the growing epidemic of cancer in young people, a new report warns.
While some conditions decrease over the age of 65, the number of people aged 50 and under being diagnosed with the disease is increasing.

4
Experts blame junk food, obesity, environmental chemicals, antibiotics, alcohol and lack of exercise.
According to the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), cancer in people under the age of 50 has been on the rise since the 1990s.
This includes colon, uterine, prostate, breast and uterine cancer.
Currently, an estimated 18,000 people under the age of 50 are diagnosed with early-stage colon cancer in the United States each year.
And the AACR predicts that across all years, there will be two million new cases of cancer in the US by 2024.
Of particular concern is the rise in early-stage colon cancer, with rates expected to double by 2030 among 29- to 35-year-olds.
Although scientists do not know exactly why this increase is caused, they say that 40 percent of cancers are associated with risk factors that can be changed – or things that you can change.
There are six factors that are under special scrutiny when it comes to youth.
1. Junk food
Cancer is thought to be caused by a combination of your genes and environment.
But according to the report, the biggest cause of this disease in young people is what we eat.
Experts warned that a diet full of red meat and processed foods, and a lack of fresh fruit and vegetables, are responsible for more than 4.2 percent of all cancers.
They recommended limiting red meat consumption to no more than three times a week, and not eating processed meats such as bacon, salami and hot dogs at all.
“These foods may increase the risk of colon and other possible cancers, including bladder and pancreatic cancer,” the authors said.
They also encouraged people to think about how many sugary drinks they drank, pointing out that soda, fruit and sports drinks, as well as coffee and tea with added sugar, were linked to increased risk. of liver and colon cancer, diabetes and kidney disease.
Cancer screening in England
Catching cancer early gives you the best chance of survival, and a big part of that is getting regular screenings.
NHS programs can help diagnose the disease, or the risk of it, and improve the chance of successful treatment.
There are three national programs in England: cervical screening, breast screening and bowel screening.
“If you are eligible, please do your best to do your screening test as they can detect the problem early, before you have symptoms. , “NHS says.
“Finding a problem early can mean that treatment is more effective.”
Cervical examination
This is offered in England to people with cervical cancer aged 25 to 64 and is usually performed every three to 49 years, and every five to from 50 to 64.
Depending on the outcome, people may be recalled earlier.
During cervical screening, samples are tested for high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which causes almost all types of cervical cancer.
Those found to be infected are then tested further.
Breast examination
Breast examinations, which include an X-ray test called a mammogram that can detect cancer when it is too small to be seen or felt, are usually offered to women aged 50 to 71 in England.
But the NHS is testing them for women under 50 if they have a high risk of breast cancer.
Bowel examination
This test detects if patients are showing early signs of cancer.
It’s available to anyone aged 54 to 74, with the program gradually expanding to 50-plus following The Sun’s No Time 2 Lose campaign.
Currently, 54- to 74-year-olds are sent home screening kits every two years, so make sure your doctor has your correct address.
The home test involves giving a small sample of poo to be checked for small amounts of blood, which can be caused by cancer.
If you are aged 75 or over, you can request a kit every two years by calling the free bowel cancer screening helpline on 0800 707 60 60.
Source: NHS
In general, research shows children and older adults to have less nutritious diets than older adults.
Forty-five percent of young people reported eating fast food every day between 2013 and 2017, compared to 37 percent of adults over 40.
“Eating a healthy diet can help reduce the risk of many chronic conditions, including cancer,” the scientists wrote.
Unfortunately, compared to other age groups, the diet of young people is poor, with high consumption of foods high in fat and refined carbohydrates and low in fiber, and insufficient consumption of fruit and vegetables. vegetables.
“The lack of healthy eating among this population can be attributed to many factors, including food insecurity, family eating habits, convenience and lack of access to healthy food.
“Poor dietary habits can persist into adulthood and increase the risk of many obesity-related cancers.
“Reducing or eliminating the consumption of processed foods, fast food, and foods and beverages high in sugar is critical to curbing the obesity epidemic and reducing the burden of related cancers.”

4
2. Obesity
Obesity is responsible for 7.6 percent of all cancers, according to the report.
Among US adults, the obesity rate from 2017 to 2020 was 41.9 percent.
This is an increase of 37 percent from the year 2000, when the rate was 30.5 percent.
“During this same period, obesity among US adults nearly doubled, with an increase from 4.7 to 9.2 percent,” the authors wrote.
“Globally, obesity rates doubled between 1990 and 2022, with 16 percent of adults over the age of 18 being obese by 2022.
“The increasing prevalence of other risk factors, including obesity among US children and adults, is a cause for public health concern.
Like smoking, obese adults are at increased risk of many chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, stroke and cancer.
They add that weight-loss measures, such as surgery and medication, have been successful in reducing or eliminating obesity-related cancer risk.
Although more research is needed, studies have shown that long-term use of drugs such as Ozempic in patients with diabetes has reduced the risk of colon cancer by half compared to insulin.
4
3. Chemicals in the environment
The AACR report also highlights the risk of exposure to chemicals in the environment.
This can include pollutants found in the air, drinking water and food, “which make them difficult to avoid”.
However, some people are exposed to high levels of certain substances, such as arsenic, asbestos, radon, lead and radiation, due to their lifestyles or occupations.
“Exposure to higher than acceptable levels of environmental chemicals, without proper protection, can increase the risk of cancer,” the scientists said.
For example, they said radon – a naturally occurring radioactive gas produced by the decay of uranium in soil, rock and water – is responsible for 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year – with 2,900 in people who are do not smoke.
“Those who live in urban areas, especially those with low economic status, are exposed to high levels of other traffic-related pollutants, which are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer,” they added.
4. Use of antibiotics
When was the last time you took antibiotics?
The report warns that taking the medicine, which is used to treat bacterial infections, for a long time can increase the chances of getting cancer.
Research has shown that people under the age of 50 who take antibiotics are 1.5 times more likely to develop colon cancer than those over the age of 50.
“Although the mechanisms of this increase are not well understood, researchers believe that antibiotics destroy the normal bacteria in the gut, called the microbiome, disrupting the careful balance that promotes a healthy digestive system ,” the report said.
4
5. Alcohol
Most of us know that alcohol is not good for us.
But the ACCR report warns that it is one of the reasons for the increase in cancer in young people.
Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of six types of cancer, including head and neck, liver and colon, as well as more than 200 other diseases.
In the United States in 2019, 5.4 percent of cancers were caused by alcohol.
Some studies show that people who drink a lot of alcohol in their youth increase the chances of being diagnosed with colon cancer before the age of 50 by 150 percent.
However, there is good news. Research also shows that those who reduce or stop drinking alcohol have an eight percent lower risk of alcohol-related cancer, and a four percent lower risk of all cancers compared to those who do not. still drinking or increasing it.
6. Sedentary behavior
Finally, living a sedentary lifestyle may increase the risk of certain cancers, the report warns.
“For example, researchers found that a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer increased proportionally for every hour spent watching television,” the authors wrote.
“The study also showed that the more TV a person watched, the higher their BMI, which explains why sedentary behavior such as watching TV increases the risk of pancreatic cancer.”
Different studies have found that compared to those who did not exercise, women reduced their chances of developing breast cancer by 18 percent with moderate exercise, 31 percent with moderate exercise, and 40 percent with of high fitness.
#lifestyle #factors #driving #cancer #epidemic #risk